astm a192
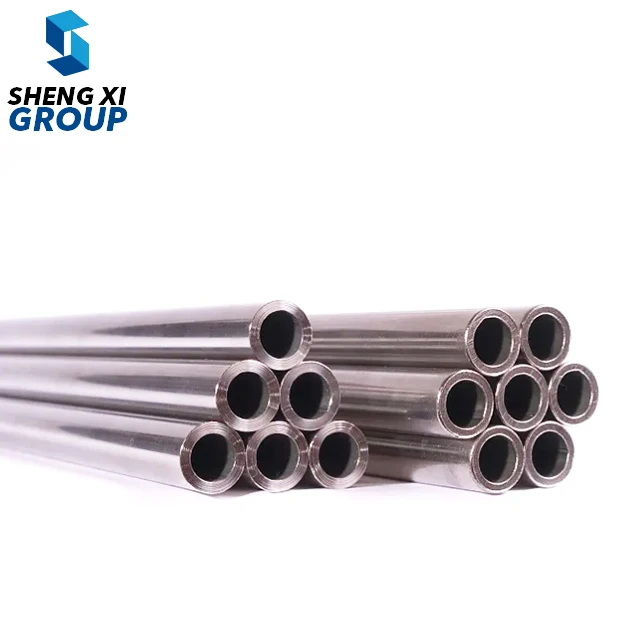
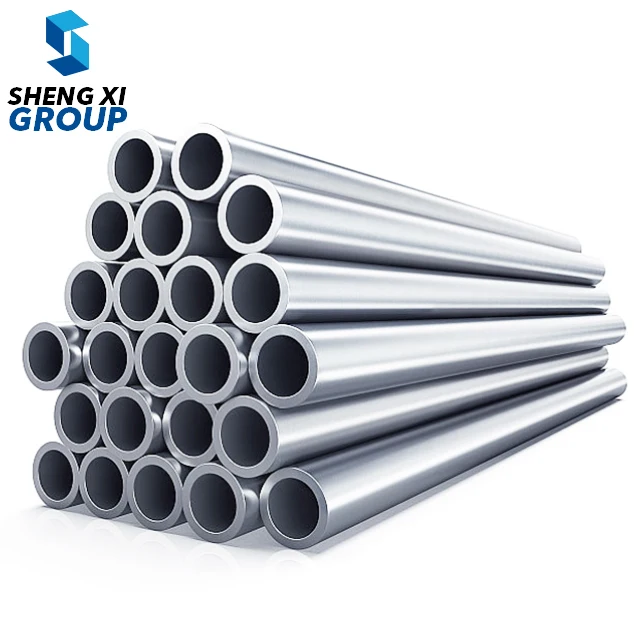
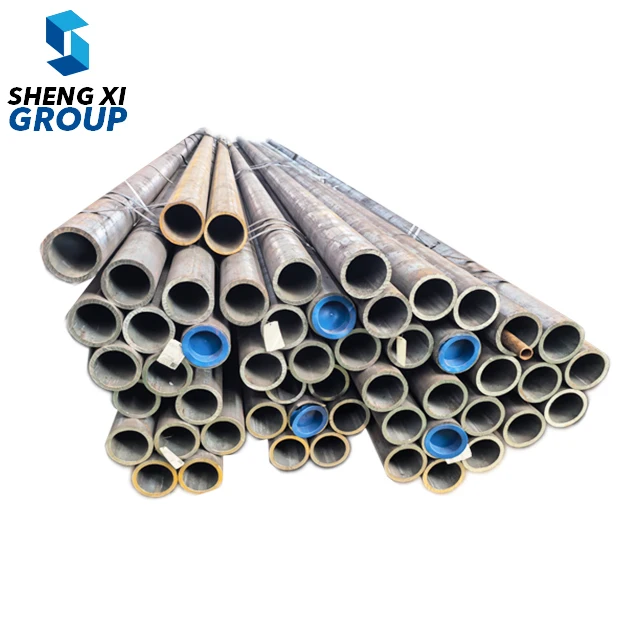
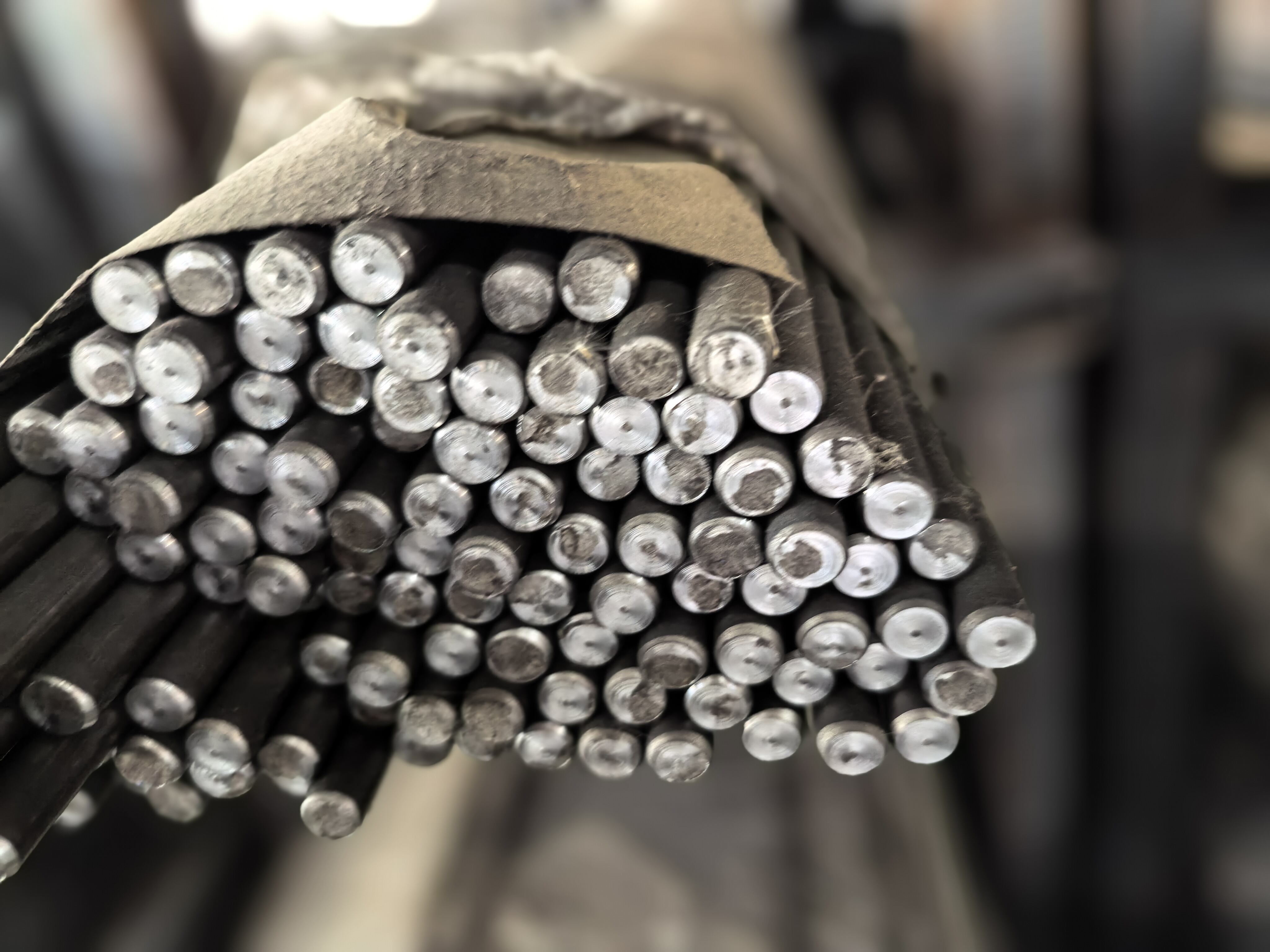
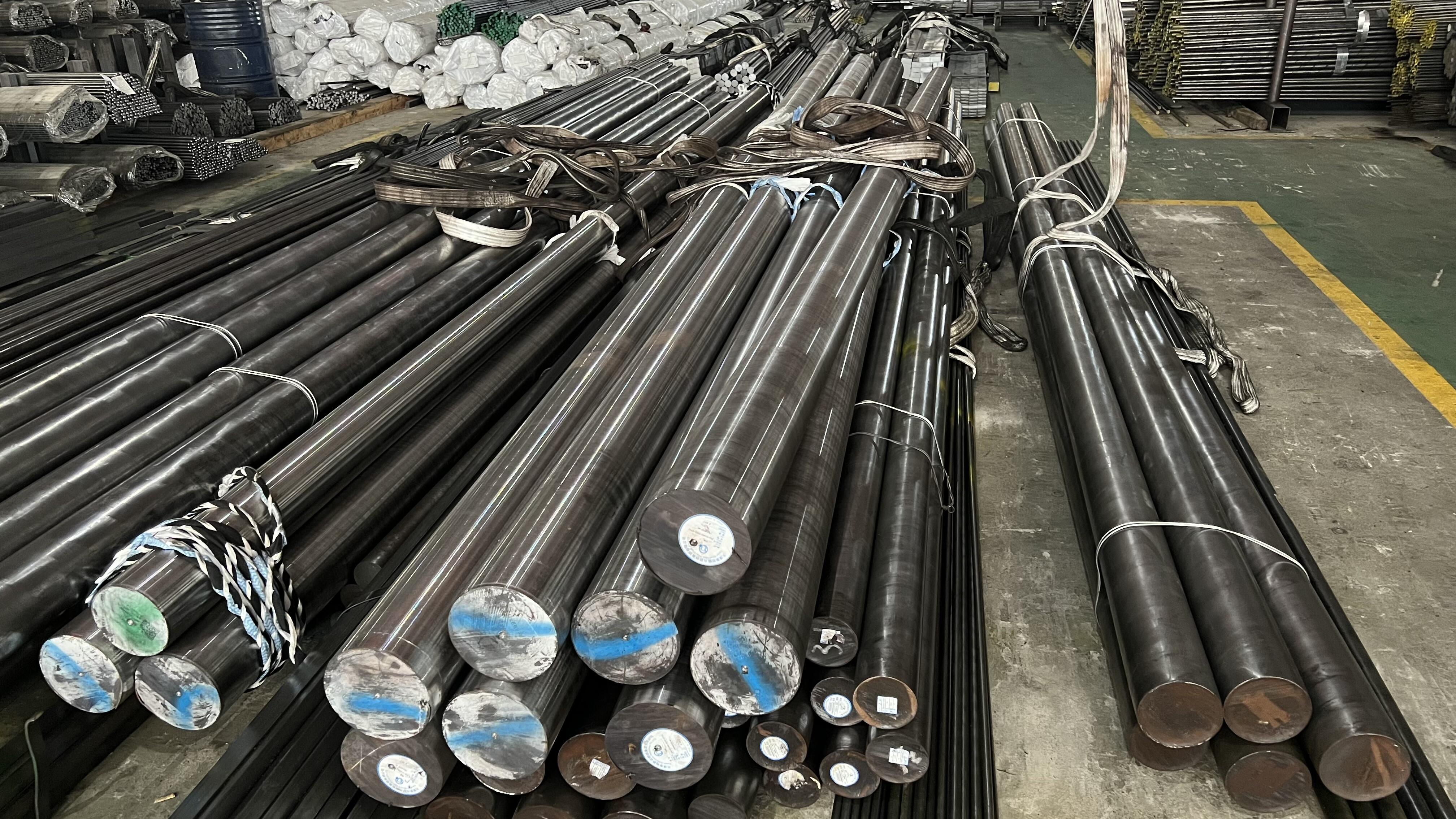
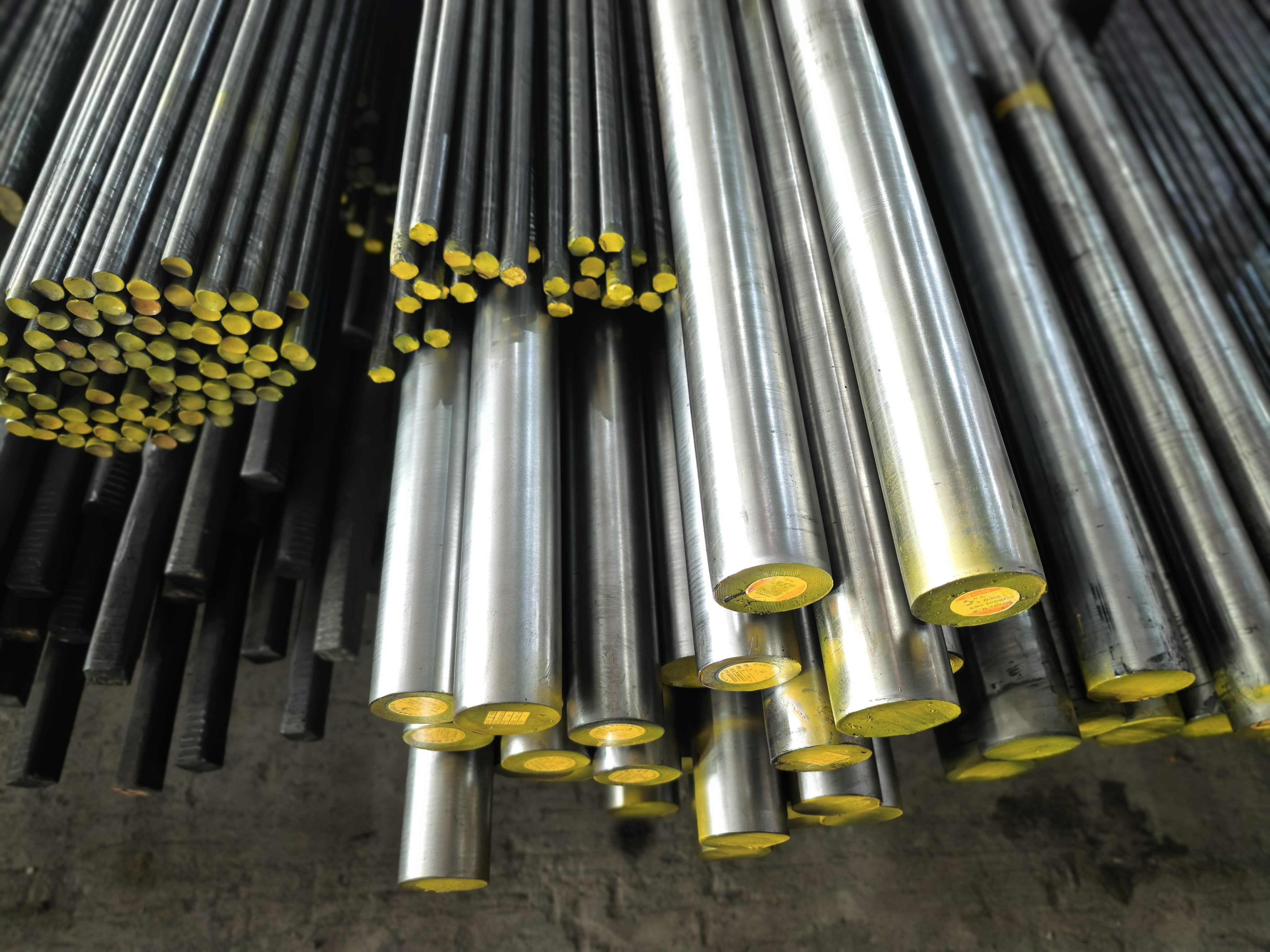
ASTM A192 is a comprehensive specification that establishes the requirements for seamless carbon steel boiler tubes designed for high-pressure service applications. This specification covers tubes manufactured through hot-finished or cold-drawn processes, primarily utilized in steam generation systems where reliability and performance are paramount. The ASTM A192 standard ensures that these carbon steel tubes meet stringent quality requirements for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional accuracy. These tubes are engineered to withstand elevated temperatures and pressures commonly encountered in power generation facilities, industrial boilers, and steam systems. The specification mandates specific carbon content levels and mechanical strength characteristics that enable the tubes to maintain structural integrity under demanding operating conditions. ASTM A192 tubes are manufactured using carefully controlled processes that ensure uniform wall thickness, precise dimensional tolerances, and consistent material properties throughout the entire length of each tube. The standard requires comprehensive testing procedures including hydrostatic testing, flattening tests, and tensile strength evaluations to verify that each tube meets the established performance criteria. These carbon steel boiler tubes are designed with excellent heat transfer capabilities, making them ideal for applications where efficient thermal conductivity is essential. The specification also addresses surface finish requirements, ensuring that the tubes have smooth internal surfaces that minimize friction losses and prevent scale buildup during operation. ASTM A192 tubes undergo rigorous quality control measures during manufacturing, including non-destructive testing methods to detect any potential defects or inconsistencies. The standard provides guidelines for proper marking and identification of tubes, enabling easy traceability and quality assurance throughout the supply chain. These tubes are available in various sizes and wall thicknesses to accommodate different system requirements and operating parameters, making them versatile solutions for diverse industrial applications.