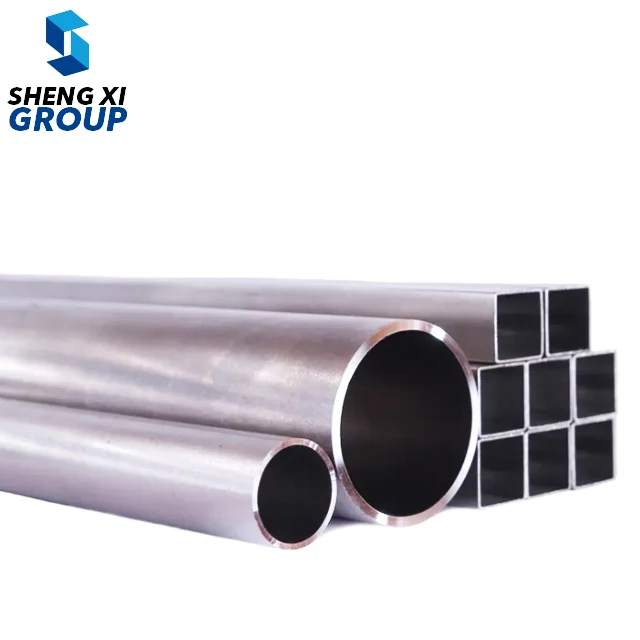
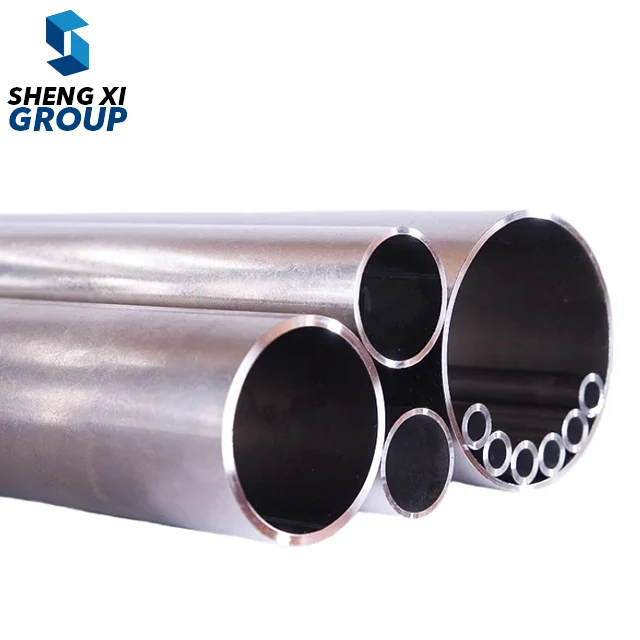
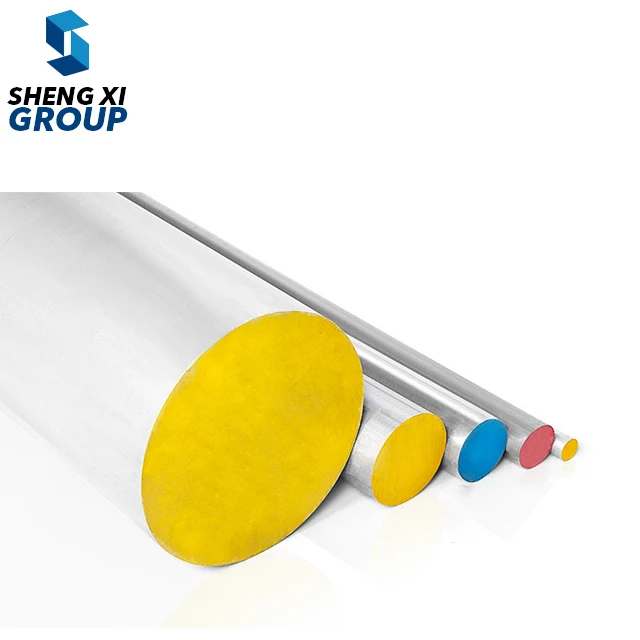
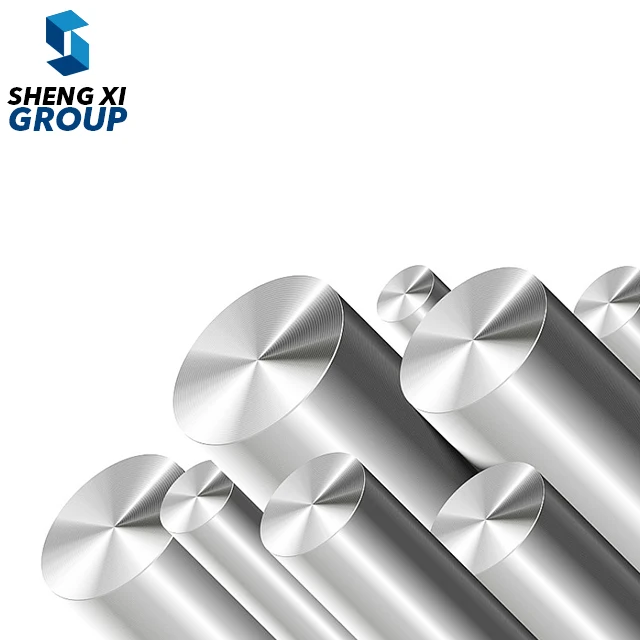
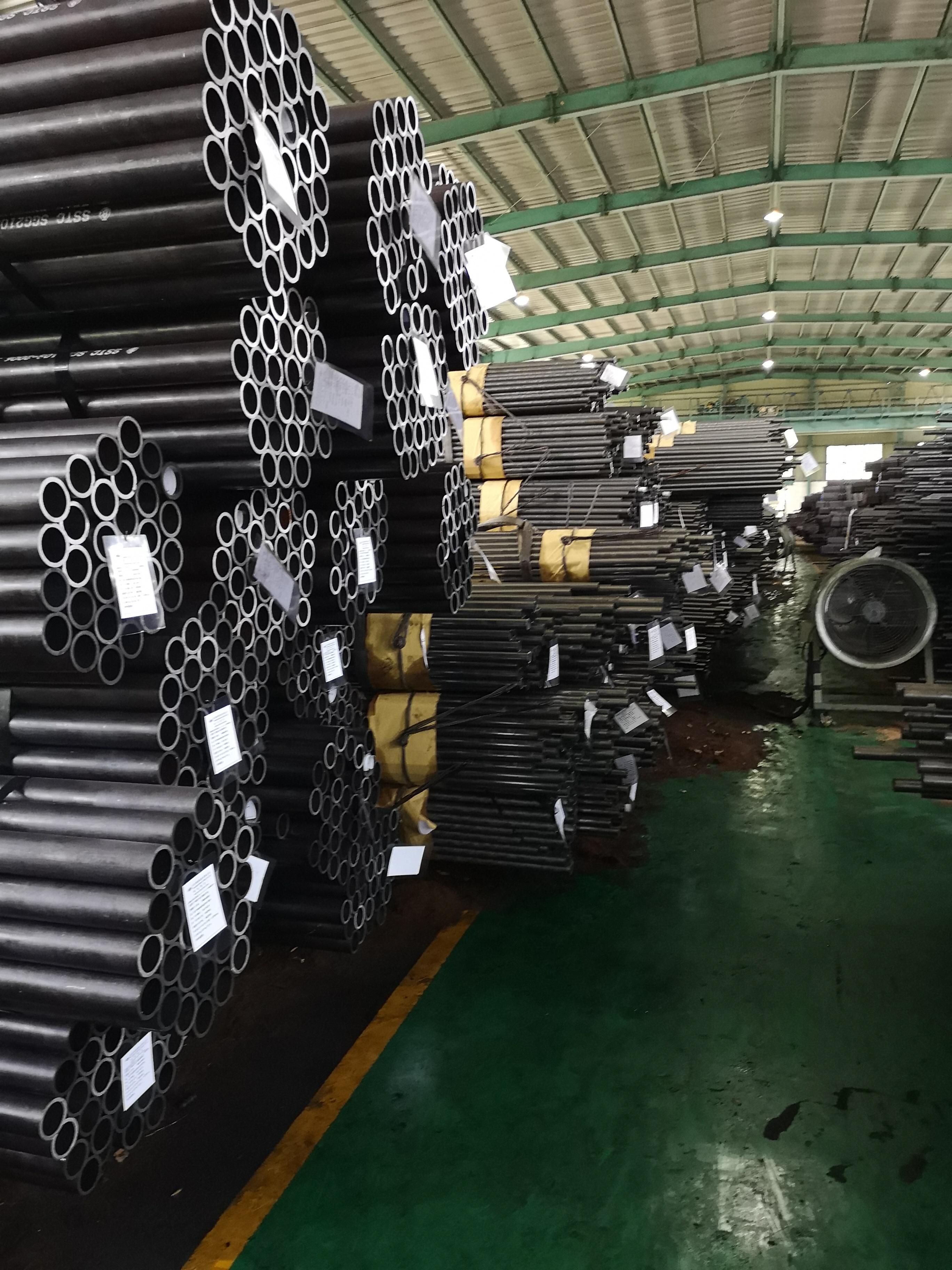
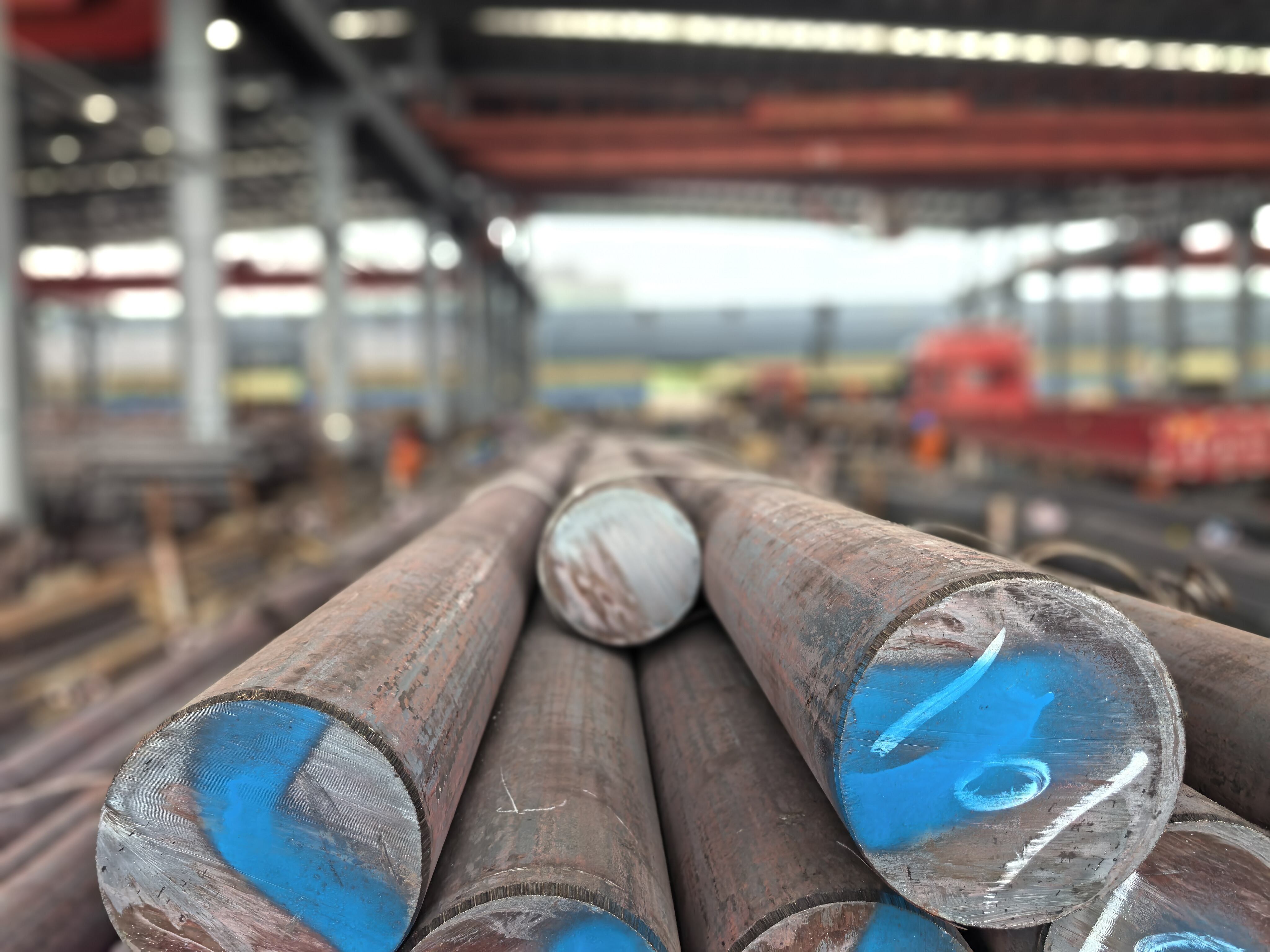
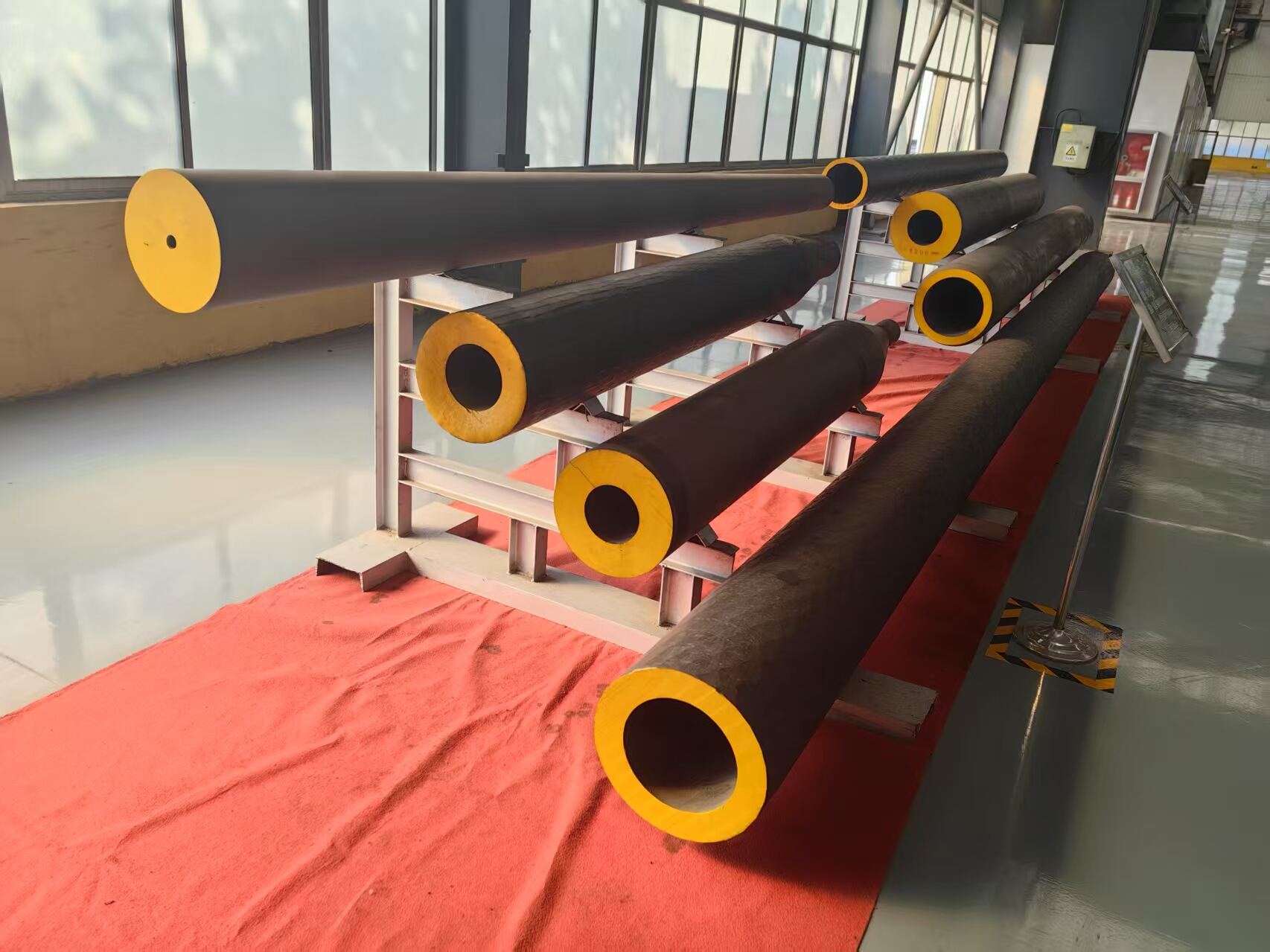
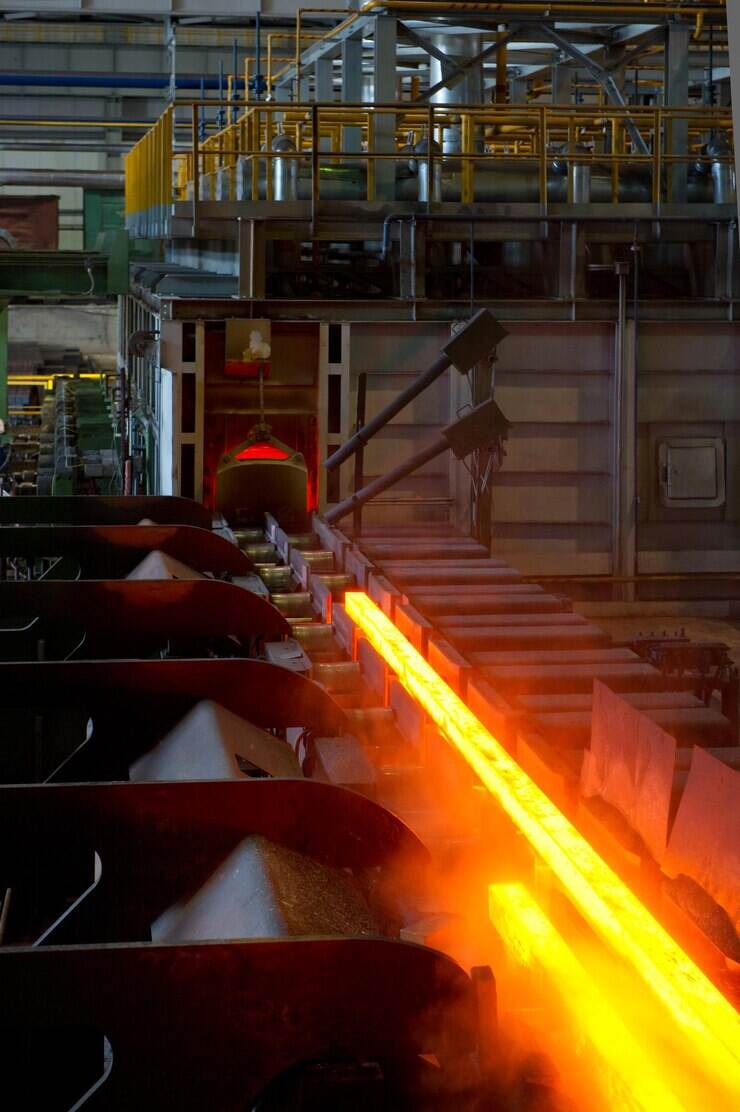
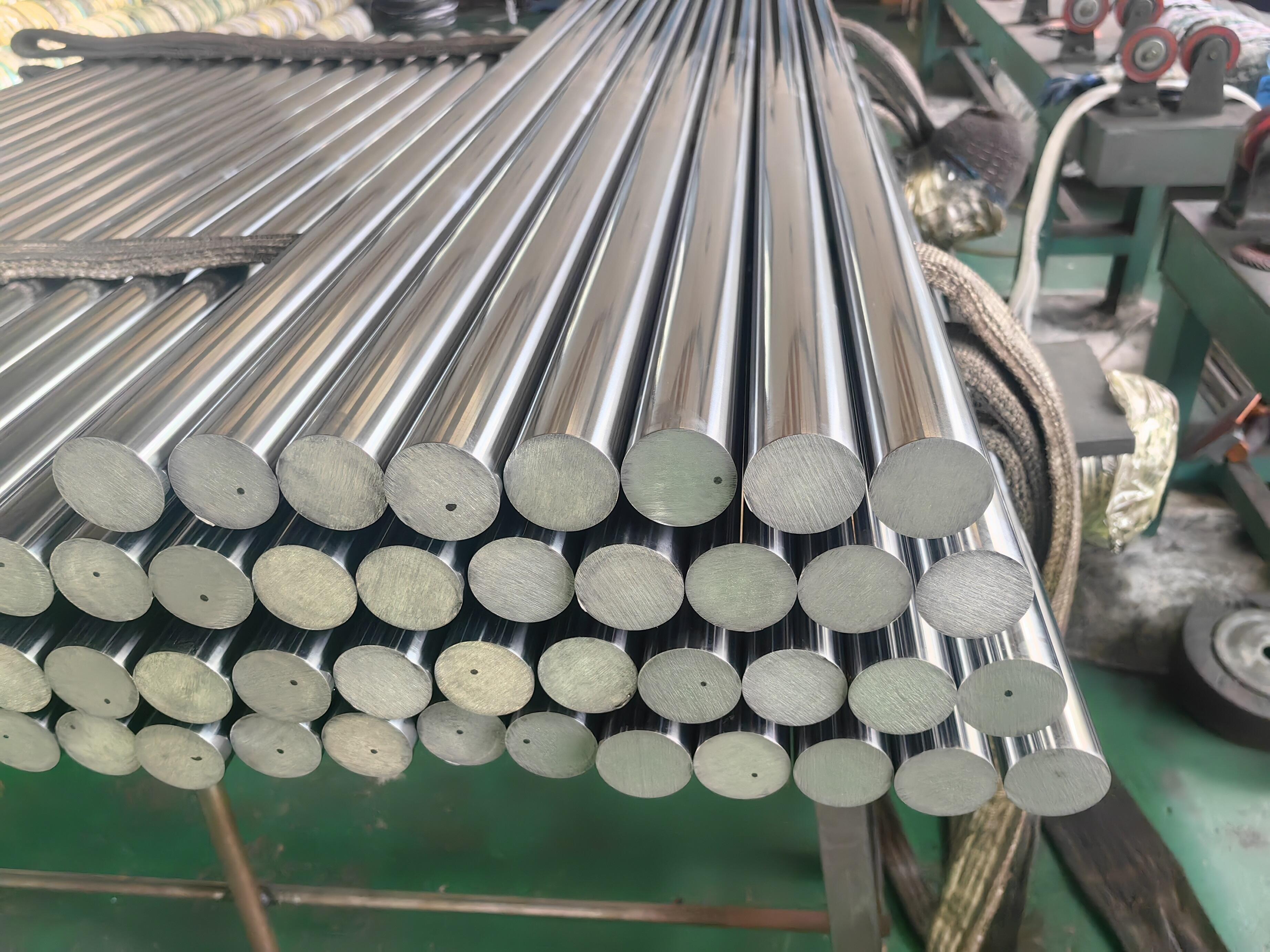
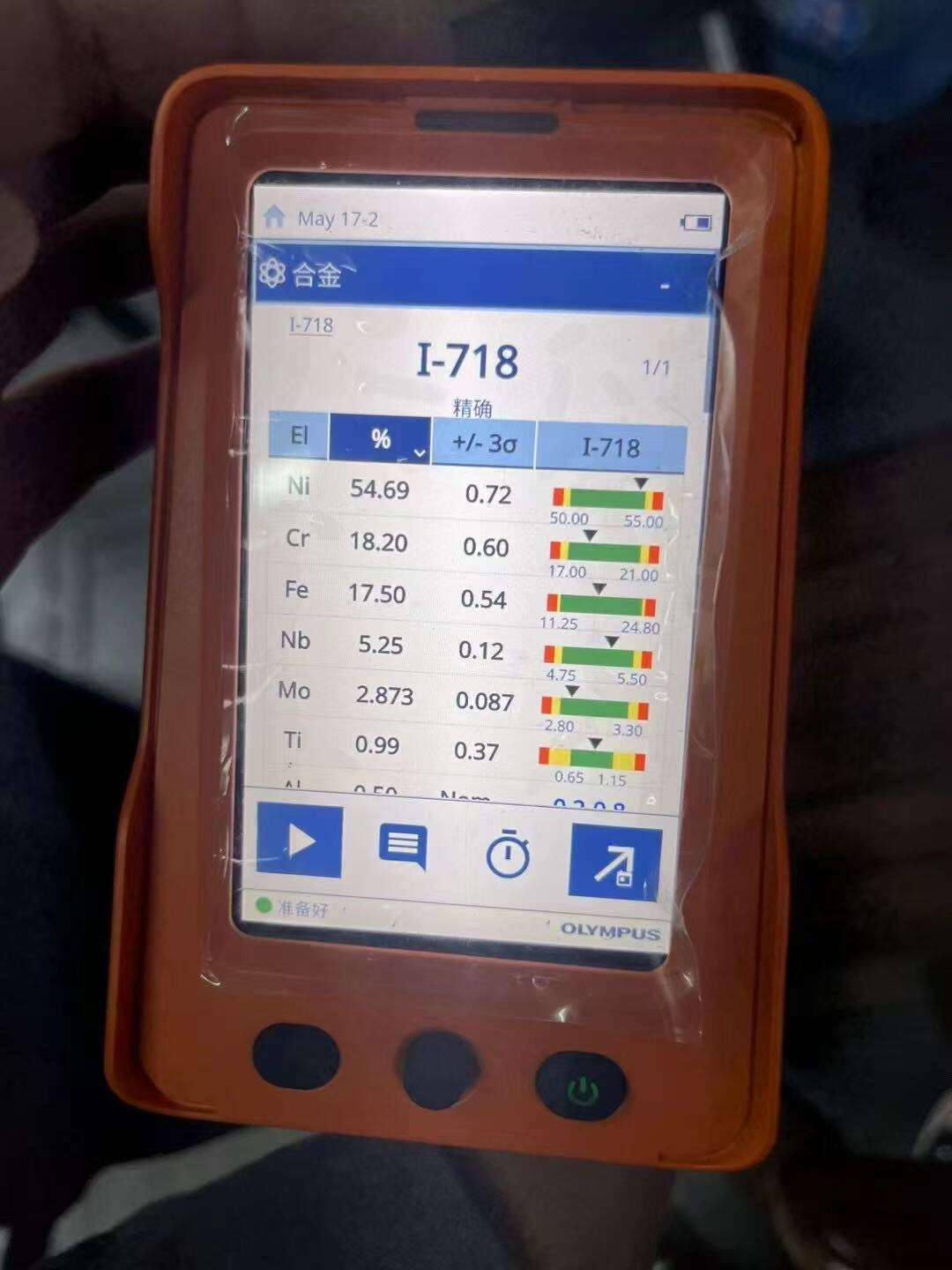
high temperature alloys
High temperature alloys represent a specialized class of metallic materials engineered to maintain exceptional mechanical properties and structural integrity under extreme thermal conditions. These sophisticated alloys are specifically designed to withstand temperatures ranging from 500°C to over 1200°C while preserving their strength, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability. The primary function of high temperature alloys centers on providing reliable performance in environments where conventional materials would fail catastrophically due to thermal degradation, oxidation, or mechanical breakdown. These materials incorporate advanced metallurgical principles, utilizing carefully balanced compositions of base metals such as nickel, cobalt, or iron, combined with strategic additions of chromium, aluminum, titanium, and other alloying elements. The technological features of high temperature alloys include superior creep resistance, which prevents gradual deformation under sustained stress at elevated temperatures. They exhibit remarkable oxidation and corrosion resistance through the formation of protective oxide layers that shield the underlying material from environmental attack. Additionally, these alloys maintain excellent fatigue resistance, allowing them to endure repeated thermal cycling without developing critical crack propagation. The microstructural design of high temperature alloys often incorporates precipitation strengthening mechanisms, where secondary phases provide enhanced mechanical properties throughout the operating temperature range. Applications for high temperature alloys span numerous critical industries, including aerospace propulsion systems, power generation turbines, petrochemical processing equipment, automotive exhaust systems, and industrial furnace components. In gas turbine engines, these materials enable higher operating temperatures, directly translating to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. The nuclear industry relies on high temperature alloys for reactor components that must withstand both extreme temperatures and radiation exposure while maintaining structural integrity over extended service periods.