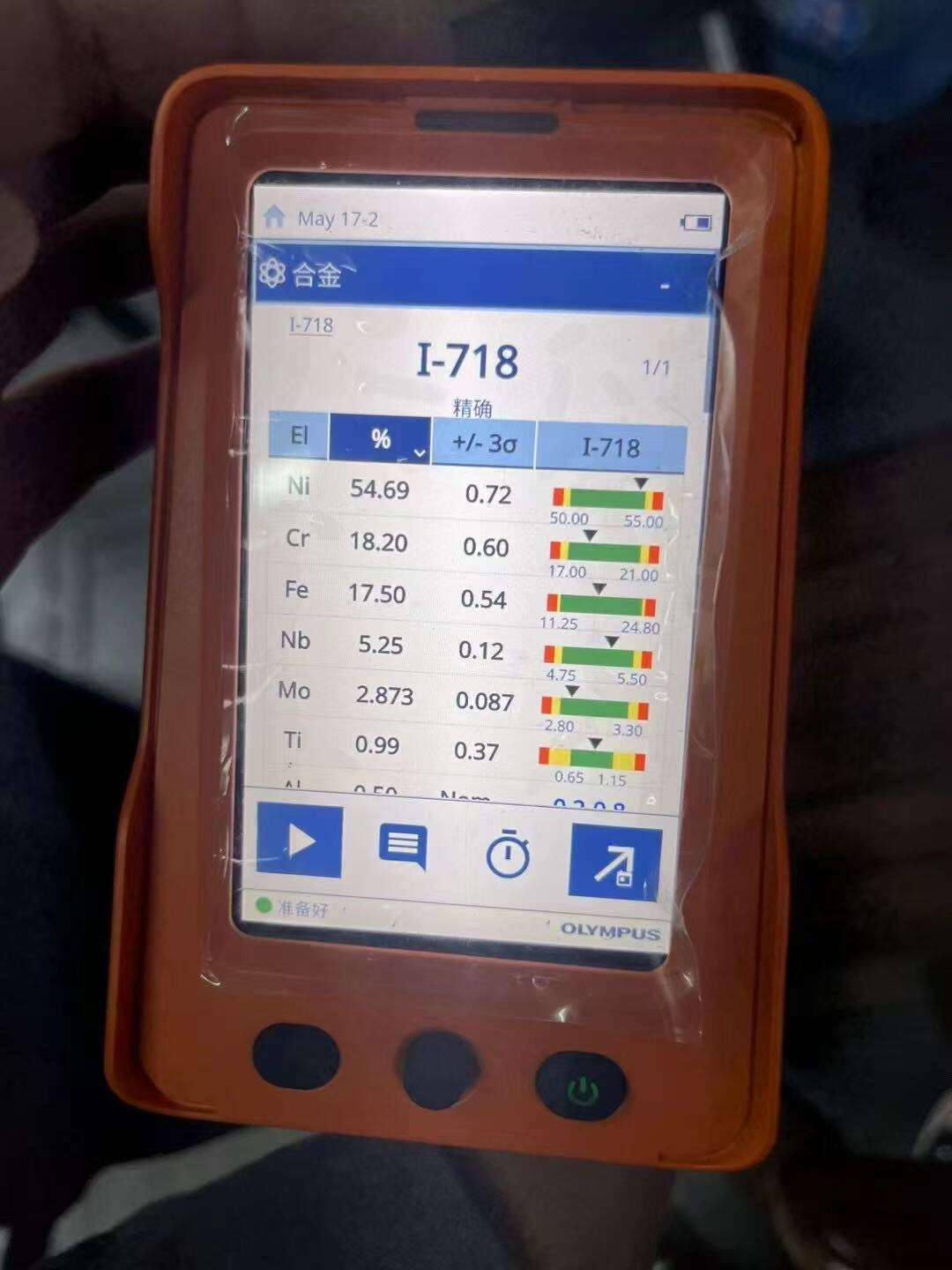
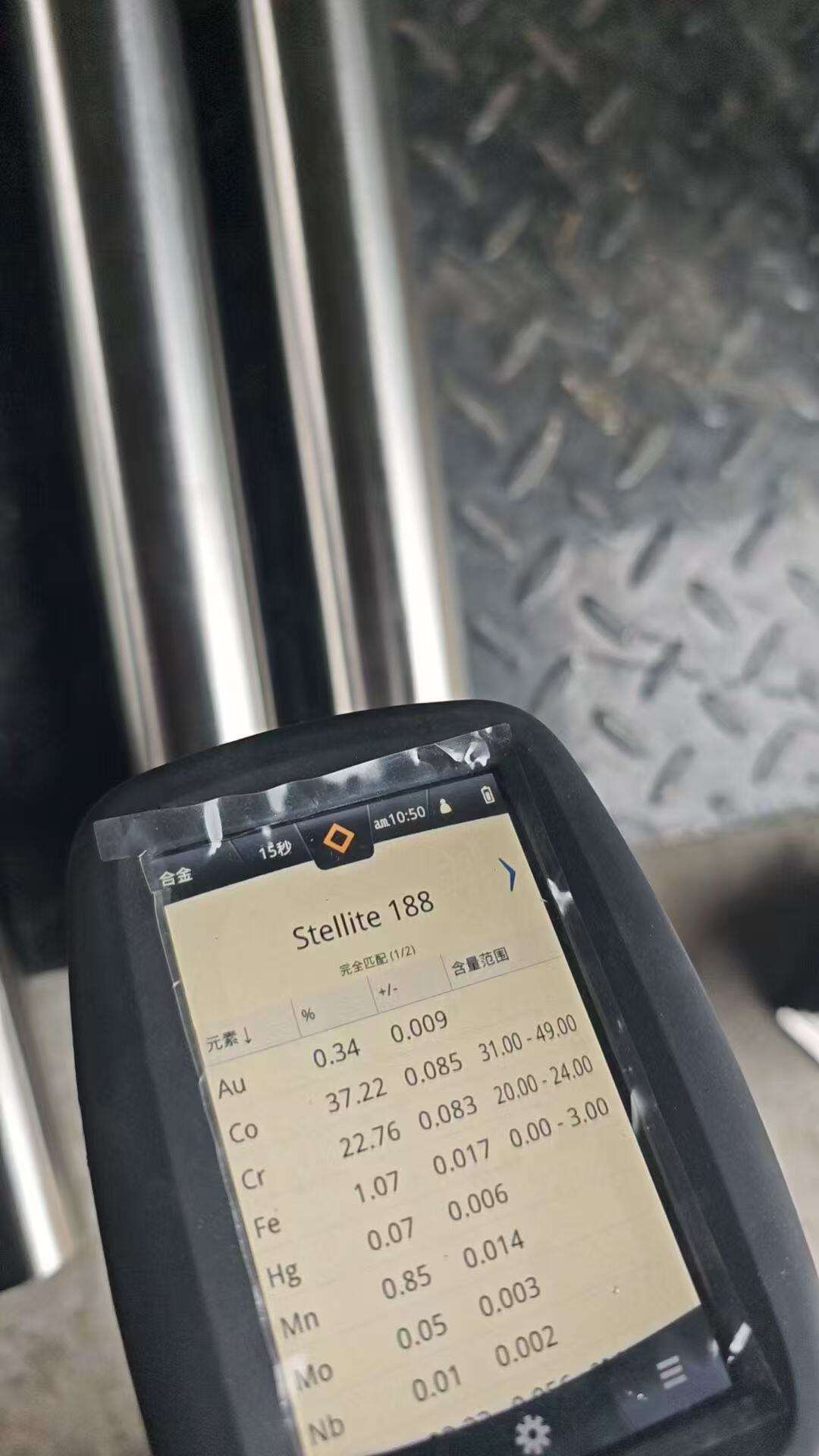
inconel temperature range
The inconel temperature range represents one of the most critical specifications for high-performance nickel-chromium superalloys, determining their effectiveness in extreme operational environments. Inconel alloys demonstrate exceptional performance across a broad temperature spectrum, typically operating efficiently from cryogenic conditions as low as -423°F (-253°C) up to extraordinary high temperatures reaching 2000°F (1093°C) or higher, depending on the specific alloy composition. This remarkable inconel temperature range makes these materials indispensable for applications requiring superior metallurgical properties under thermal stress. The main functions of inconel temperature range specifications include providing engineers and designers with precise operational parameters for material selection, ensuring optimal performance in high-temperature applications, and guaranteeing structural integrity across diverse thermal conditions. The technological features that enable this impressive inconel temperature range include advanced metallurgical compositions featuring nickel as the primary element, enhanced with chromium for oxidation resistance, and additional alloying elements such as molybdenum, tungsten, and titanium for strength enhancement. These superalloys maintain their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability throughout their specified inconel temperature range, making them superior to conventional stainless steels and carbon steels. Applications leveraging the inconel temperature range span across aerospace propulsion systems, where jet engine components must withstand extreme thermal cycling, chemical processing equipment operating under corrosive high-temperature conditions, nuclear power generation facilities requiring materials that maintain integrity under radiation and heat, and marine engineering projects exposed to saltwater corrosion and temperature fluctuations. The inconel temperature range also proves essential in industrial furnace construction, heat exchangers, and gas turbine manufacturing, where consistent performance across varying thermal conditions directly impacts operational efficiency and safety standards.